

^ Descotes, Jacques Choquet-Kastylevsky, Geneviève (February 2001)."Guideline on the investigation and management of acute transfusion reactions Prepared by the BCSH Blood Transfusion Task Force". ^ Tinegate, Hazel Birchall, Janet Gray, Alexandra Haggas, Richard Massey, Edwin Norfolk, Derek Pinchon, Deborah Sewell, Carrock Wells, Angus Allard, Shubha (October 2012).Allergy, Asthma, and Clinical Immunology. "An introduction to immunology and immunopathology". There are three main mechanisms of injury in type II reactions: (1) activation of complement followed by complement-mediated lysis or phagocytosis and removal. Antonetti, Francesca Romana (10 November 2011). Type II or cytotoxic hypersensitivity depends on the abnormal production of IgG or IgM directed against tissue antigens or a normal reaction to foreign antigens expressed on host cells. ^ a b Warrington, Richard Watson, Wade Kim, Harold L.However, there are questions as to the relevance of the Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions in modern-day understanding of allergy and it has limited utility in clinical practice. Īn example of anti-receptor type II hypersensitivity (also classified as type V hypersensitivity) is observed in Graves disease, in which anti-thyroid stimulating hormone receptor antibodies lead to increased production of thyroxine. Īnother example of a complement dependent type II hypersensitivity reaction is Goodpasture's syndrome, where the basement membrane (containing collagen type IV) in the lung and kidney is attacked by one's own antibodies in a complement mediated fashion. Ring structures for penicillins (A), cephalosporins (B), carbapenems (C), and. These reactions are not mediated by IgE, and timing of symptoms may differ (Table 2). Complement-dependent type II hypersensitivity can also occur during the transmission of incompatible maternal antibodies to fetal red blood cells causing hemolytic anemia in the fetus, known as erythroblastosis fetalis. Delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions (types II, III, and IV) are those in which the onset is 1 hour or more after drug expo-sure. Type III hypersensitivity reaction also known as immune complex hypersensitivity is the antigen-antibody complex mediated destruction of cells.
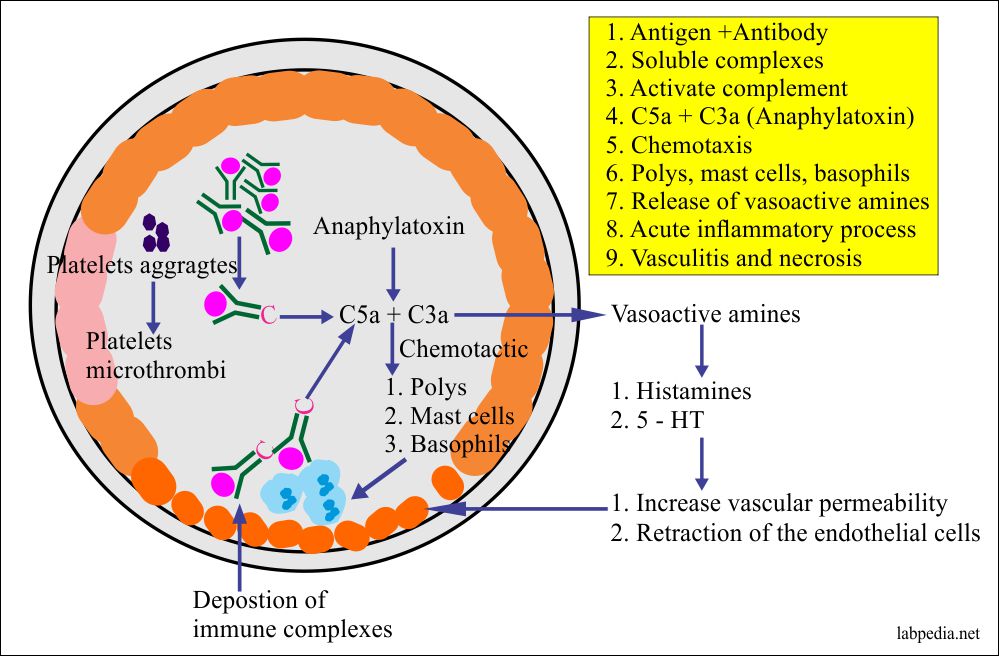
anti-A IgM in an individual with blood group B), bind to the donor red cell surface and lead to rapid complement mediated haemolysis and potentially life-threatening clinical consequences. Type I, II and III are immunoglobulin-mediated (immediate) hypersensitivity reactions while type IV reaction is lymphoid cell-mediated or simply cell mediated hypersensitivity (delayed-type). Preformed antibody (predominantly IgM) against donor red cell antigens not found in an individual of a particular blood group (e.g.

An example of complement dependent type II hypersensitivity is an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction following transfusion of ABO incompatible blood.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
